알고리즘
[Algorithm] Flood Fill (+BFS)
래울
2024. 1. 31. 09:43
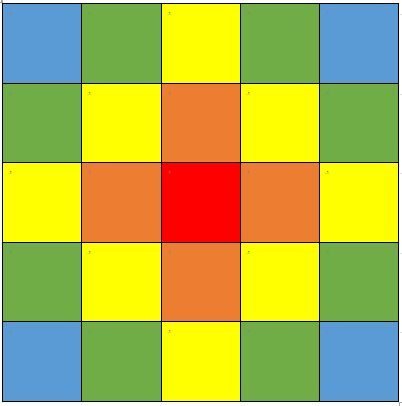
Flood Fill
- 흘러넘치다, 채우다.
- 다차원 배열에서 시작점과 연결된 영역들을 찾는 알고리즘
- 2차원 이상의 배열에서 이루어지는 BFS
- 즉 특정 좌표 (y, x) 상에 있는 노드 기준으로 BFS 탐색하는 방법
* Ex. 지도 상에서 최단 경로를 구할 때
BFS 설계
1. 큐 생성
2. 시작점을 큐에 push()
3. 큐 맨앞의 값을 확인 front()
4. pop()
5. 다음 경로들 탐색
6. 다음 경로들을 큐에 push()
7. 3 ~ 6 과정 반복
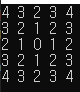
Flood Fill Example Code
- BFS와 동일하지만, 노드로 (y, x) 좌표를 가진다.
- 또한 방향 배열을 통해 퍼져나갈 영역을 정의해두고 탐색한다.
* C++에서는 struct 키워드를 생략가능
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int y;
int x;
};
int main()
{
int N = 5;
int arr[5][5];
int check[5][5];
int dy[4] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
int dx[4] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
memset(check, 0, sizeof(int) * N * N);
queue<Node> q;
q.push({ 2, 2 });
check[2][2] = 1;
int depth = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
int qSize = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < qSize; ++i)
{
Node curr = q.front();
q.pop();
arr[curr.y][curr.x] = depth;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k)
{
int y = curr.y + dy[k];
int x = curr.x + dx[k];
if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && x < N && y < N && check[y][x] == 0)
{
q.push({ y, x });
check[y][x] = 1;
}
}
}
depth ++;
}
//Print
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
{
cout << arr[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}